Introduction:
The automotive industry has witnessed significant advancements in technology over the years, with one of the critical innovations being the transition from traditional carburetors to modern fuel injection systems. Fuel injection systems play a pivotal role in optimizing engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control in vehicles. This article explores the evolution of the automotive fuel injection system market, highlighting key trends, challenges, and future prospects.
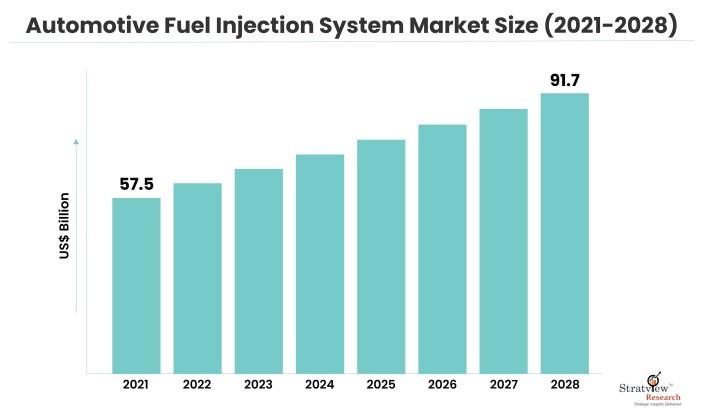
The automotive fuel injection system market is likely to grow from USD 57.5 billion in 2021 to reach USD 91.7 billion by 2028 at a healthy CAGR of 6.65% during the forecast period.
Read more: https://www.stratviewresearch.com/139/automotive-fuel-injection-system-market.html
Historical Perspective:
Historically, carburetors were the standard components responsible for mixing air and fuel in internal combustion engines. However, as the need for more precise control over fuel delivery and combustion efficiency grew, fuel injection systems emerged. The first electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems were introduced in the 1950s, primarily in racing cars and high-performance vehicles.
Evolution of Fuel Injection Systems:
Mechanical Fuel Injection:
Early fuel injection systems were primarily mechanical, utilizing pumps and injectors driven by the engine's mechanical components. While these systems offered improved fuel distribution, they lacked the flexibility and precision of modern electronic systems.
Introduction of Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI):
The 1980s saw a widespread adoption of electronic fuel injection systems, which relied on electronic control units (ECUs) to manage fuel delivery. This transition marked a significant improvement in terms of efficiency, emissions control, and overall engine performance.
Direct Fuel Injection (DI):
In the pursuit of enhanced efficiency and power, direct fuel injection systems became popular. DI systems deliver fuel directly into the combustion chamber, allowing for finer control over the air-fuel mixture. This technology is prevalent in modern gasoline and diesel engines.
Current Market Trends:
Hybridization and Electrification:
With the rise of electric and hybrid vehicles, fuel injection systems are evolving to complement these technologies. Hybrids often incorporate advanced fuel injection strategies to optimize combustion in internal combustion engines, providing a seamless transition between electric and combustion modes.
Advanced Electronic Control:
Ongoing advancements in electronic control systems and sensors contribute to more precise fuel injection strategies. Real-time data from various engine parameters allow for adaptive fuel delivery, optimizing performance under different driving conditions.
Emission Standards Compliance:
Stricter global emission standards drive continuous innovation in fuel injection technology. Manufacturers are focusing on developing systems that not only improve fuel efficiency but also reduce harmful emissions, aligning with environmental regulations.
Challenges:
Cost Constraints:
The integration of advanced fuel injection technologies can pose cost challenges for manufacturers. Striking a balance between performance improvements and affordability remains a key concern.
Complexity and Maintenance:
Modern fuel injection systems are intricate and require specialized knowledge for diagnostics and repairs. This complexity can lead to higher maintenance costs and challenges for technicians.
Future Outlook:
Continued Integration with Advanced Technologies:
Fuel injection systems will likely continue to integrate with other advanced automotive technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and connectivity, to enhance overall vehicle performance.
Enhanced Efficiency and Alternative Fuels:
Future fuel injection systems may focus on optimizing efficiency with alternative fuels, including biofuels, hydrogen, and synthetic fuels, as the industry seeks more sustainable solutions.
Autonomous Vehicles:
As autonomous vehicles become more prevalent, fuel injection systems may adapt to the unique demands of self-driving cars, optimizing fuel delivery based on driving scenarios and energy requirements.
Conclusion:
The automotive fuel injection system market has undergone a remarkable evolution, from mechanical systems to sophisticated electronic and direct injection technologies. As the industry continues to prioritize efficiency, emissions control, and performance, the future of fuel injection systems will likely be shaped by advancements in electrification, artificial intelligence, and alternative fuels. Manufacturers and researchers will play a crucial role in addressing challenges and steering the market toward a more sustainable and technologically advanced future.