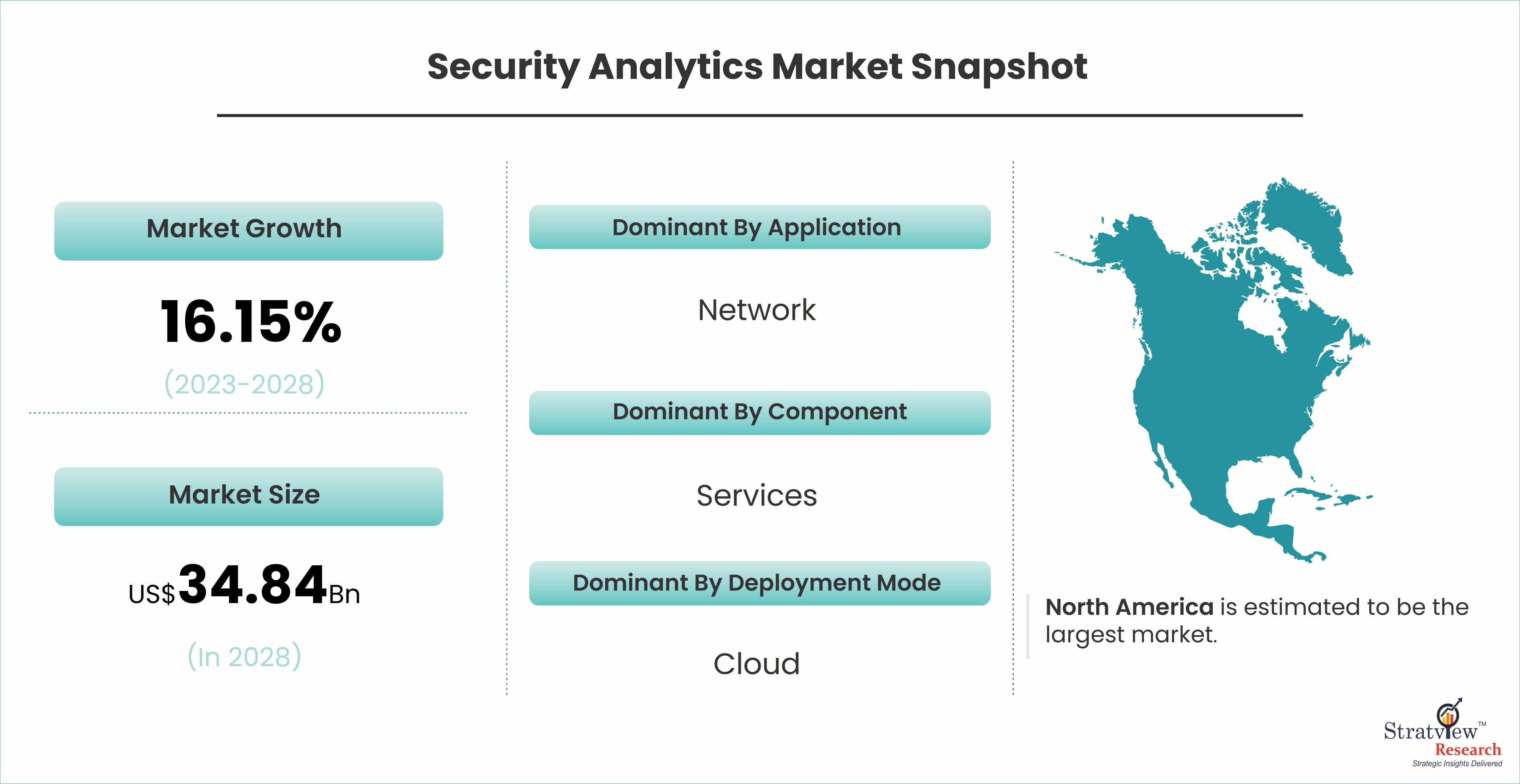
According to Stratview Research, the security analytics market was estimated at USD 14.13 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 16.15% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 34.84 billion in 2028.
In the digital age, where cyber threats are constantly evolving and growing in sophistication, organizations are compelled to look beyond traditional defense mechanisms. Beyond the firewall lies a dynamic and expansive realm known as the Security Analytics Landscape. This landscape represents a paradigm shift in cybersecurity, leveraging advanced technologies to analyze vast datasets, decode threats, and fortify digital fortresses. In this article, we embark on a journey to explore the insights offered by the Security Analytics Landscape and understand its pivotal role in modern cybersecurity.
The Limitations of Traditional Security Measures:
Traditional security measures, such as firewalls and antivirus software, play a crucial role in preventing known threats from entering a network. However, they often fall short in addressing the rapidly changing nature of cyber threats. Advanced persistent threats (APTs), zero-day exploits, and insider threats require a more sophisticated and proactive approach that extends beyond the traditional firewall.
The Shift to Proactive Defense: The Security Analytics Landscape represents a shift from reactive to proactive defense strategies. Rather than solely focusing on preventing known threats, security analytics embraces the analysis of data patterns, behaviors, and anomalies to detect potential threats in real-time. This proactive stance is essential in a landscape where cyber adversaries are continuously adapting and innovating their tactics.
Real-Time Threat Detection: One of the key insights offered by the Security Analytics Landscape is real-time threat detection. By continuously monitoring network activities and analyzing vast amounts of data, security analytics platforms can identify anomalies and potential security incidents as they unfold. This real-time insight enables organizations to respond swiftly and effectively, minimizing the impact of cyber threats.
Behavioral Analytics and Anomaly Detection: Behavioral analytics is a cornerstone of the Security Analytics Landscape. By establishing a baseline of normal user behavior, security analytics tools can detect deviations and anomalies that may indicate malicious activity. This approach goes beyond signature-based detection methods, allowing organizations to identify novel and previously unseen threats.
Integrated Threat Intelligence: The Security Analytics Landscape integrates threat intelligence feeds, enriching the analysis with up-to-date information about known threats, vulnerabilities, and adversary tactics. This integration empowers organizations to contextualize security events, understand the broader threat landscape, and prioritize their response efforts based on the latest intelligence.
Forensic Analysis and Incident Response: In the aftermath of a security incident, the Security Analytics Landscape provides valuable insights for forensic analysis and incident response. Security analytics platforms capture detailed information about the attack vectors, entry points, and lateral movements within the network. This information is crucial for understanding the extent of a breach and fortifying defenses against future incidents.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: Machine learning and artificial intelligence are driving transformative changes in the Security Analytics Landscape. These technologies enable systems to autonomously learn from data, identify complex patterns, and predict potential threats. The adaptive nature of machine learning enhances the accuracy of threat detection and response, providing a dynamic defense against evolving cyber threats.
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): User and Entity Behavior Analytics is a specialized area within the Security Analytics Landscape that focuses on understanding the behavior of users and entities within a network. UEBA helps identify anomalies, insider threats, and compromised accounts by analyzing patterns of activity and highlighting deviations from established norms.
Future Trends and Challenges:
As organizations continue to navigate the Security Analytics Landscape, future trends include the increasing adoption of cloud-based security analytics, enhanced automation for rapid response, and collaborative threat intelligence sharing. However, challenges such as the shortage of skilled professionals, data privacy concerns, and the need for effective integration with existing security infrastructure remain on the horizon.
Conclusion:
Beyond the firewall, the Security Analytics Landscape offers invaluable insights that redefine the way organizations approach cybersecurity. By embracing proactive defense strategies, leveraging real-time threat detection, and harnessing the power of advanced technologies, organizations can strengthen their resilience against a constantly evolving threat landscape. The Security Analytics Landscape is not just a tool; it's a mindset that empowers organizations to stay one step ahead in the perpetual cat-and-mouse game of cybersecurity. As we delve deeper into this landscape, we unlock the potential to decode, mitigate, and fortify – ensuring a secure digital future beyond the traditional confines of the firewall.