The liquid biopsy market is revolutionizing the field of cancer diagnostics and personalized medicine. By analyzing circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and circulating tumor cells (CTCs) from a simple blood sample, liquid biopsies offer a non-invasive alternative to traditional tissue biopsies. This innovative approach allows for early cancer detection, real-time monitoring, and tailored treatment strategies. However, while the liquid biopsy market holds immense promise, it also faces significant challenges. In this article, we explore the key challenges and opportunities in the liquid biopsy market that stakeholders need to know.
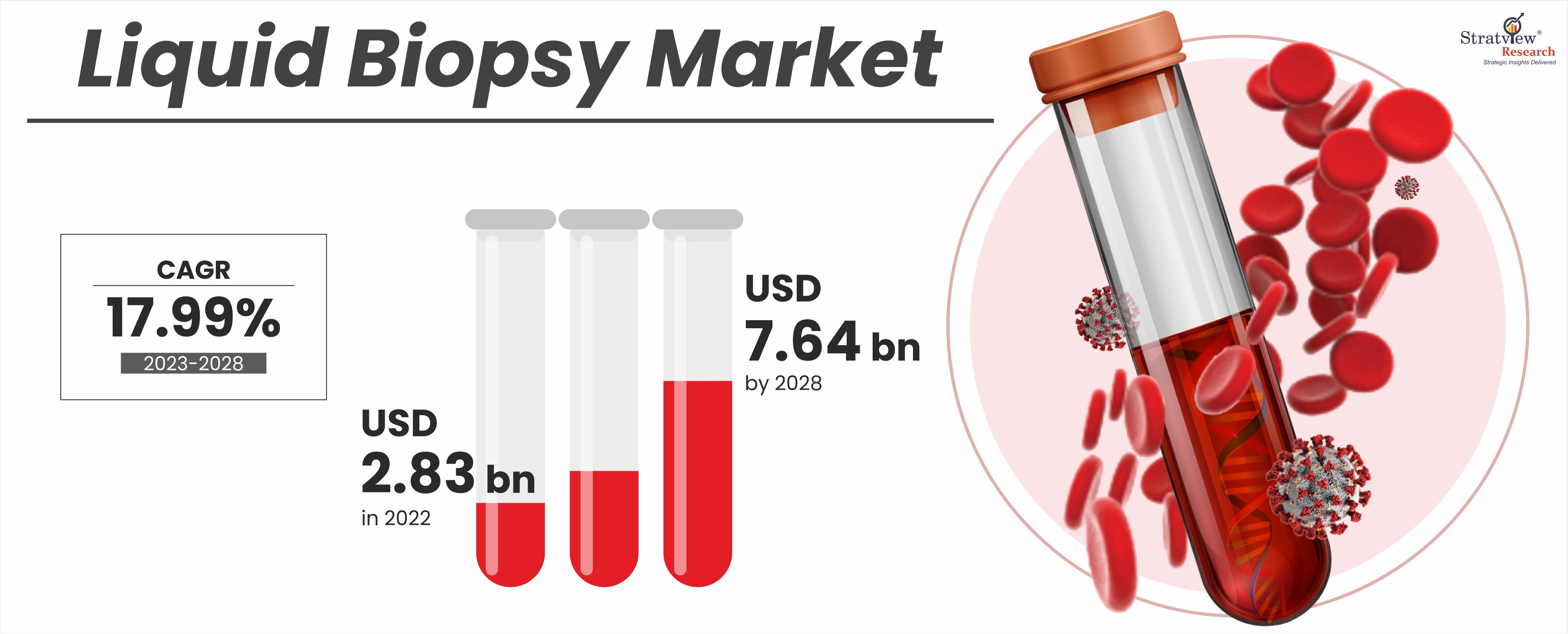
According to Stratview Research, the liquid biopsy market was estimated at USD 2.83 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 17.99% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 7.64 billion in 2028.
Opportunities in the Liquid Biopsy Market
Early Cancer Detection and Diagnosis
Liquid biopsies have the potential to detect cancer at its earliest stages, often before symptoms appear. Early detection is crucial for improving patient outcomes and survival rates. By identifying ctDNA or CTCs in the bloodstream, liquid biopsies can diagnose cancer earlier than traditional methods.
Non-Invasive Monitoring of Disease Progression
Unlike traditional biopsies, which are invasive and can only be performed at specific intervals, liquid biopsies can be conducted frequently with minimal discomfort to the patient. This allows for continuous monitoring of ctDNA levels, providing real-time insights into disease progression and treatment efficacy. It enables oncologists to make timely adjustments to treatment plans based on the patient's response.
Personalized Treatment Strategies
Liquid biopsies provide detailed genetic information about a tumor’s mutations and alterations. This genetic profiling helps oncologists select the most effective targeted therapies and immunotherapies based on the specific molecular characteristics of the cancer. Tailoring treatment to the individual patient's genetic profile enhances the efficacy of therapies and reduces adverse effects.
Detection of Minimal Residual Disease (MRD)
Liquid biopsies are valuable in detecting minimal residual disease (MRD), which refers to the small number of cancer cells that may remain in the body after treatment. By identifying ctDNA at very low levels, liquid biopsies can detect MRD earlier than traditional imaging methods, allowing for prompt intervention and potentially preventing cancer recurrence.
Broadening Applications Beyond Oncology
While the primary focus of liquid biopsies has been on cancer, their applications are expanding into other areas of medicine. Researchers are exploring the use of liquid biopsies for monitoring organ transplant rejection, detecting prenatal genetic abnormalities, and identifying infectious diseases. This broadening scope opens new avenues for early diagnosis and personalized treatment in various medical fields.
Challenges in the Liquid Biopsy Market
Technical and Analytical Challenges
Despite significant advancements, liquid biopsies still face technical challenges related to the sensitivity and specificity of detecting ctDNA and CTCs. Tumor DNA is often present in very low quantities in the bloodstream, making it difficult to detect accurately. Ensuring that liquid biopsy tests are highly sensitive and specific is crucial for reliable results.
Standardization and Regulatory Approval
The lack of standardized protocols and guidelines for liquid biopsy testing presents a significant challenge. Different laboratories may use varying methods and technologies, leading to inconsistencies in results. Achieving regulatory approval for liquid biopsy tests requires demonstrating their accuracy, reliability, and clinical utility. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA are working to establish clear guidelines, but the process can be lengthy and complex.
Reimbursement and Cost Issues
Securing reimbursement from healthcare payers is essential for the widespread adoption of liquid biopsies. However, demonstrating the cost-effectiveness of these tests can be challenging. Healthcare systems and insurance companies need robust evidence of the clinical benefits and economic value of liquid biopsies. The high cost of developing and conducting these tests also poses a barrier to accessibility.
Integration into Clinical Practice
Integrating liquid biopsies into routine clinical practice requires overcoming several hurdles. Healthcare providers need to be educated about the benefits and limitations of liquid biopsies and trained in their interpretation and use. Additionally, the healthcare infrastructure must be equipped to handle the processing and analysis of liquid biopsy samples.
Data Interpretation and Management
The genetic data generated by liquid biopsies can be complex and vast. Interpreting this data accurately requires advanced bioinformatics tools and expertise. Ensuring that the data is managed securely and used ethically is also crucial, particularly given the sensitive nature of genetic information.
Conclusion
The liquid biopsy market is poised for significant growth, offering numerous opportunities for early cancer detection, personalized treatment, and real-time monitoring of disease progression. However, the market also faces considerable challenges, including technical and analytical hurdles, regulatory and reimbursement issues, and the need for standardization and integration into clinical practice.
Addressing these challenges will require collaborative efforts from researchers, healthcare providers, regulatory bodies, and industry stakeholders. By overcoming these obstacles, the liquid biopsy market can realize its full potential, transforming cancer care and personalized medicine, and ultimately improving patient outcomes. For investors, healthcare professionals, and patients alike, staying informed about the evolving landscape of liquid biopsies is essential as we move towards a new era of non-invasive, precision diagnostics.