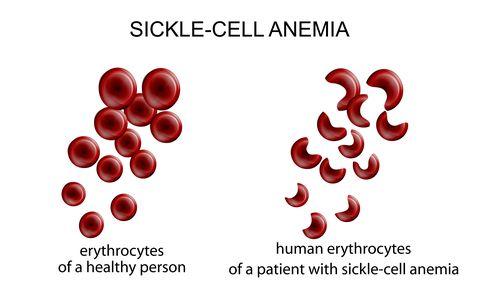
Overview of Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited blood disorder that affects hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein within red blood cells. It causes red blood cells to become rigid and form into a sickle, crescent, or other abnormal shape instead of the usual soft, plump round shape. These misshapen cells have difficulty passing through small blood vessels, which can slow or block normal blood flow and oxygen delivery throughout the body. These sickled cells also tend to break apart and die early, causing a constant shortage of red blood cells.
Methods for Testing and Screening
Several types of tests are available for screening and diagnosing sickle cell anemia. These include:
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
A CBC is usually the first laboratory test done to detect Sickle Cell Anemia Screening and Testing. It measures the number of red blood cells and checks them for abnormal shapes, sizes, and other characteristics. An abnormal CBC may indicate the presence of sickle cells.
Hemoglobin Electrophoresis
This test separates different types of hemoglobin in the blood based on their electric charge and identifies variants like hemoglobin S. It is considered the Gold standard confirmatory test for sickle cell disease.
Get More Insights on- Sickle Cell Anemia Testing and Screening